News
Tertiary-educated adults with autism receive training for jobs in engineering sector


Tertiary-educated adults with autism are being trained and placed in jobs in the engineering sector under a new programme by research and technology non-profit organisation Trampolene.
The Gates (Growing Autistic Talent for Engineering Sector) programme was started in May 2022, after research showed that people with autism have one of the lowest employment rates among people with disabilities.
Those with tertiary qualifications also face underemployment owing to a high entry barrier for higher-skilled jobs, said Trampolene chief operating officer Cheok Xue Ting.
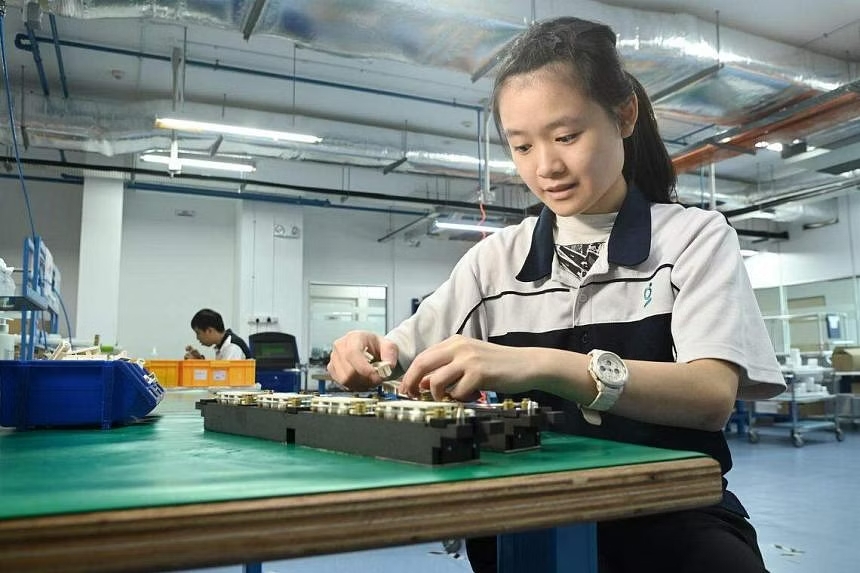
Ms You Kai Xuan is among 42 graduates of institutes of higher learning enrolled in the programme. She was unable to secure internships as part of her studies at the Institute of Technical Education (ITE) as companies told the school she was unsuitable.
The 22-year-old, who has a Nitec in infocomm technology, is working full-time as an assembly technician at precision manufacturing company Grand Venture Technology (GVT).
Young adults with autism lack executive function skills, such as planning and time estimation.
Ms Hillary Lim, who works for Trampolene as a senior job coach, helped create a timetable for Ms You. It details specific duties she must undertake. For example, it says Ms You has to test iron bars for 90 minutes from 8.30am, and “pack silver things in plastic bags and paste stickers on the bags” between 10.15am and 11.40am.
Ms Lim also held Ms You’s hand during the coaching to show her how much strength was needed when using a torque screwdriver.
Ms You needs the timetable to pace herself and manage her time. When she started working in 2022, she tired herself out before lunch as she exerted too much strength on simple tasks.
“At first, I was nervous as I was new to the environment. But I am comfortable with the supervisor and colleagues now. They guided me patiently on the tasks, and were caring and willing to help.”
The Gates programme is the first to be supported by Temasek Foundation under a pay-for-success model.
The $340,000 committed by upfront funders will be repaid if trainees stay in a job for nine months and other outcomes of job training and placement are achieved.
In this funding model, foundations, financial institutions and corporations provide upfront capital to organisations like Trampolene to serve their beneficiaries.
Outcome funders such as the Government repay upfront funders only if the project achieves outcome targets.
Ms Cheok said the pay-for-success model focuses on retention rate, an issue among young adults with autism, who tend to leave their jobs after six months.
Before the job placement, Trampolene assessed Ms You and found her suitable for hands-on work.
Ms Lim also briefed Ms You’s colleagues on how she communicates, telling them that they need to repeat or simplify instructions.
She told them they can also break down the work into small steps and share her responsibilities.
GVT chief executive Julian Ng said one of the main challenges the company encountered was communication. Some staff with autism take what others say literally and have trouble understanding abstract concepts.
For example, Ms You’s colleagues will say “I’ll get back to you by a specific time” rather than “I’ll get back to you later”.
“This improves communication for everyone in the workplace,” said Mr Ng. The company has about 150 employees at its Singapore headquarters, including three with special needs.
Trampolene also works with organisations to redesign the recruitment process and job role. With GVT, it advised the company to use work assessment instead of conventional interviews.
To match trainees with employers, Trampolene conducts tests for specific skills employers are looking for, from motor skills to data entry and quality control.
It then selects trainees able to perform the tasks, said Ms Cheok.
She said Trampolene also considers work planning, hygiene and safety awareness, and sensory challenges.
If a trainee is affected by high-frequency noises even with earplugs on, for example, he might be more suited to an office job than engineering.
Trampolene is aiming to train 70 young adults over 30 months from May 2022.
To date, it has trained 42 graduates with autism and placed 18 of them in jobs, with 13 having stayed with their employers for three months or more.
Aside from Temasek Foundation, some of the other upfront funders are Ishk Tolaram Foundation, Quantedge Foundation and Asia Philanthropic Ventures.
Outcome funders include ECCA Family Foundation and the Diana Koh Foundation through the Community Foundation of Singapore.
Mr Nicholas Tay, who has autism and holds a diploma in pharmaceutical science from Temasek Polytechnic, was hired under the programme as a production worker in ice-cream manufacturing company The Ice Cream & Cookie Co.
He sets up workstations for production, prepares packaging and places products on a conveyor system for printing or metal detection testing.Mr Damian Yip, head of production at the company, said he considered Mr Tay’s basic communication skills, education level and challenges faced at previous workplaces to decide if he was suitable for the role.
Ms Lim said Mr Tay’s main issues are perspective-taking and negative thinking. For example, when the 26-year-old began doing this job, he often felt lousy about himself when he saw others working faster than him.
“A regular person would think, ‘Oh, the person is faster than me because he has been here for a longer time than me, so he is more experienced,’” said Ms Lim.
“However, Nicholas’ thinking was: ‘Oh, that person is faster than me. I have to be as fast, if not I am not good enough to work here.’”
She said Mr Tay’s co-workers often look out for him when he shows signs that he is tired or when work is too difficult for him. They then get him to switch duties, to take the load off him.
But Mr Tay initially thought they moved him because he was not doing a good job.
Ms Lim mapped out Mr Tay’s thoughts and shared with him other possibilities – for instance, that co-workers may move him to other duties because they care about him.
“It helps to widen Nicholas’ perspectives and also lets him try to think in different ways,” she said.
To learn more about the causes CFS supports, please click here.
Source: The Straits Times © SPH Media Limited. Permission required for reproduction
- Related Topics For You: CHARITY STORIES, DONOR STORIES, DONOR-ADVISED FUND, EDUCATION, IMPROVING EMPLOYABILITY, NEWS, PARTNERSHIP STORIES, PERSONS WITH DISABILITIES, YOUTH
Trending Stories
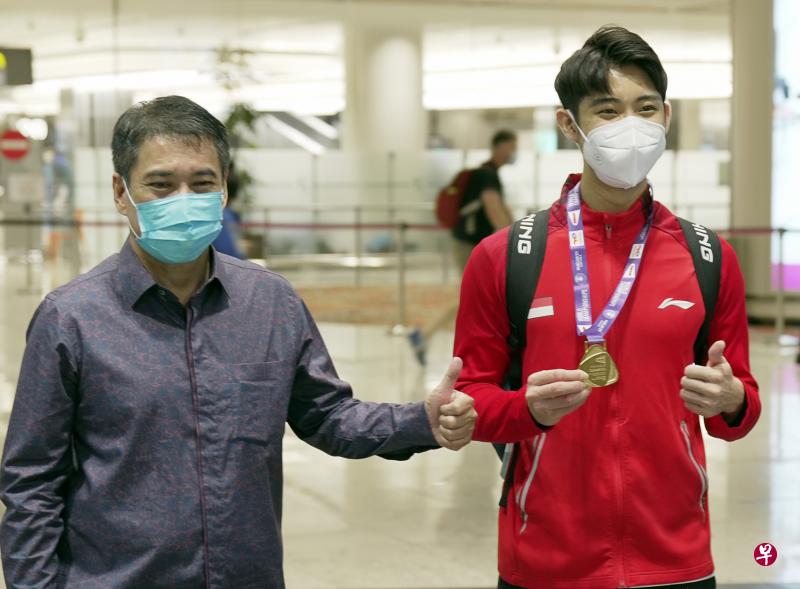


Karim Family Foundation: Donor-Advised Fund Raises $200,000 to Support Local Sports Champion Loh Kean Yew
Karim Family Foundation: Donor-Advised Fund Raises $200,000 to Support Local Sports Champion Loh Kean Yew
In December 2021, 24-year-old Loh Kean Yew became the first Singaporean to win the Badminton...

‘I thought I couldn’t go through any more of it’: Cancer patient gets help after insurer says ‘no’ to $33k bill
‘I thought I couldn’t go through any more of it’: Cancer patient gets help after insurer says ‘no’ to $33k bill
Good Samaritans have stepped forward to help a cancer patient, who hopes to spend more...